Type 1 diabetes - basic notions
T1D and T2D
Home / Type 1 diabetes / T1D and T2D
Type 1 diabetes
versus
Type 2 diabetes
Most people know at least one person with diabetes – a great uncle, a young neighbour. The disease is often described as a worldwide epidemic with a growing number of reported cases each year. Despite such incidence, diabetes is still not very well known. For instance, how many people know that there are different “types” of diabetes? And who is not taken aback when they learn that a child or a teenager is diabetic? Let’s review the facts and rectify some common myths.
This disease, often described as an epidemic, is frequently misunderstood due to assumptions and misinformation. The media and people in general are rarely able to explain the distinction between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes.
The Diabetic Children’s Foundation would like to increase public awareness about both types of diabetes and dispel the myths that lead to a great deal of prejudice against children. For this reason, the Foundation seeks to encourage the media, its partners and its member families to raise public awareness about young insulin-dependent diabetics.

One word, two very different realities
Type 1 diabetes
Form:
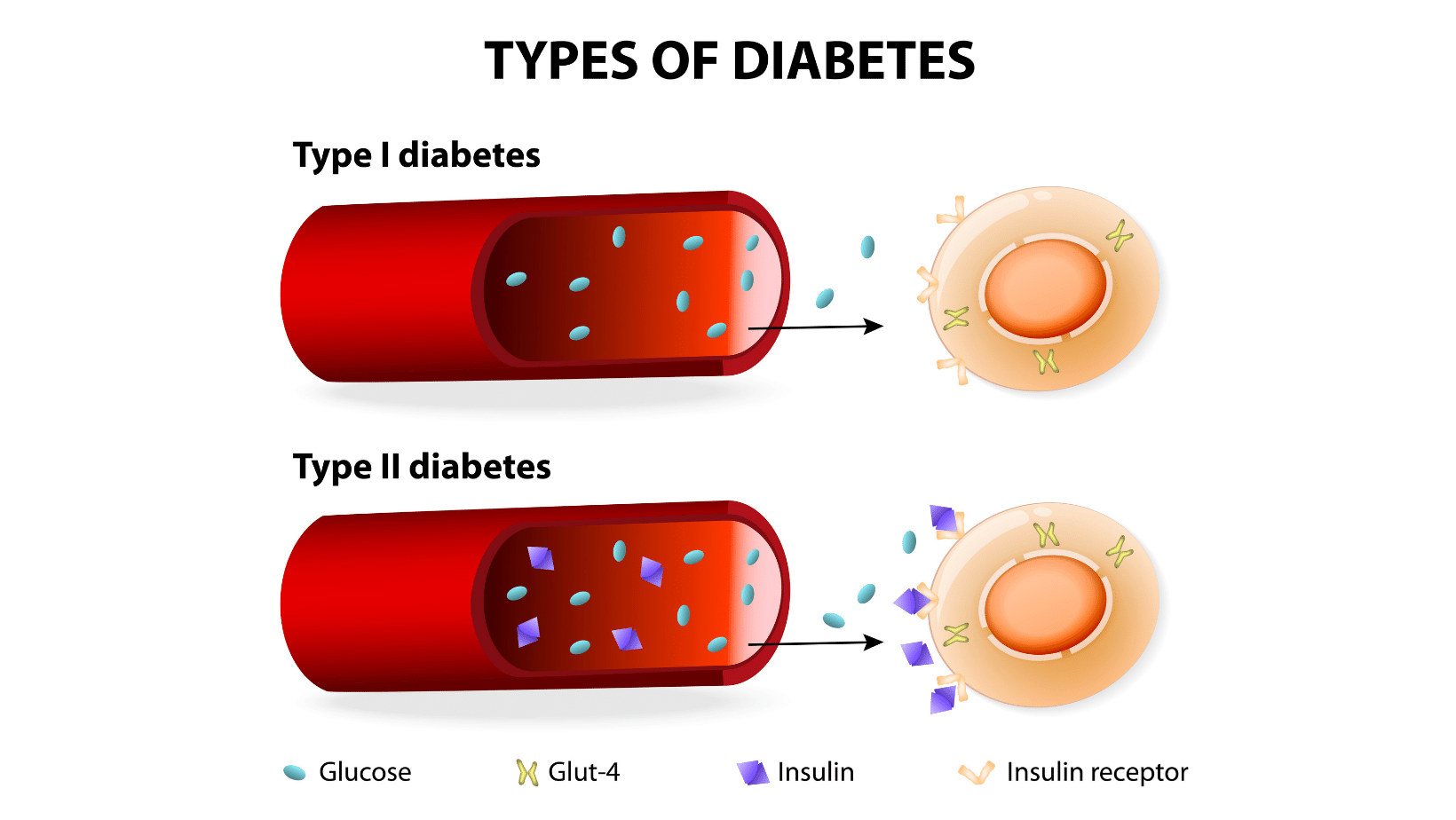
Type 1 diabetes is linked to the cessation of production of the hormone that regulates blood sugar levels, namely insulin.
Cause:
The risk of developing type 1 diabetes is greater when a family member (father, mother, brother and sister) has type 1 diabetes.
Treatments:
- Insulin injection
- Moderate-intensity
physical activity - Watch your diet
- Monitoring of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c)
- Blood pressure control
- Cholesterol monitoring
Cure:
No cure currently exists
type 2 diabetes
Form:
Type 2 diabetes, also called insulin resistant, is linked to the resistance of cells in the body to the passage of insulin (insulin resistance).
Cause:
Family background and genes are factors linked to the onset of type 2 diabetes. Physical inactivity, cholesterol, overweight and obesity increase the risk of developing the disease, without the reasons being clearly identified.
Treatments:
- Oral antidiabetics
- Drugs that stimulate
insulin production or insulin injections - Watch your diet
- Regular physical activity
- Monitoring of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c)
- Blood pressure control
- Cholesterol monitoring
Cure:
It is possible to achieve remission of the disease by making a change in life. According to a study published in the medical journal BMJ in September 2018, 15kg less would lead to total remission of diabetes. On the other hand, a particular diet restores insulin production according to a hyperglycemia study published in Cell magazine in February 2017, showing the restoration of insulin-producing pancreatic cells.
type 1 diabetes
type 2 diabetes
Form:
Type 1 diabetes is linked to the cessation of production of the hormone that regulates blood sugar levels, namely insulin.
Form:
Type 2 diabetes, also called insulin resistant, is linked to the resistance of cells in the body to the passage of insulin (insulin resistance).
Cause:
The risk of developing type 1 diabetes is greater when a family member (father, mother, brother and sister) has type 1 diabetes.
Cause:
Family background and genes are factors linked to the onset of type 2 diabetes. Physical inactivity, cholesterol, overweight and obesity increase the risk of developing the disease, without the reasons being clearly identified.
Treatments:
- Insulin injection
- Moderate-intensity physical activity
- Watch your diet
- Monitoring of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c)
- Blood pressure control
- Cholesterol monitoring
Treatments:
- Oral antidiabetics
- Drugs that stimulate insulin production or insulin injections
- Watch your diet
- Regular physical activity
- Monitoring of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c)
- Blood pressure control
- Cholesterol monitoring
Cure:
No cure currently exists
Cure:
It is possible to achieve remission of the disease by making a change in life. According to a study published in the medical journal BMJ in September 2018, 15kg less would lead to total remission of diabetes. On the other hand, a particular diet restores insulin production according to a hyperglycemia study published in Cell magazine in February 2017, showing the restoration of insulin-producing pancreatic cells.
Source
Canadian Diabetes Association
GEOFFROY, Louis Geoffroy and Monique Gonthier, Diabetes in Children, CHU Sainte-Justine, Montreal, 2009
Support for young diabetics



